Just when we thought Artificial Intelligence news flashed enough in the market. Meta-AI launched a brand new face of AI model– The Llama 3.1! What’s so great about this technology?
Well, Llama is different as compared to ChatGPT and other platforms as it is an open-source model while GPT is a proprietary model and provides more flexibility and control in collation with ChatGPT.
So, does this mean Meta Llama is better than ChatGPT? Well for that we need to deep dive into this highly intuitive comparison that weighs down some epic symmetry of both the revolutionary AI tools.
Though they serve distinct purposes, Llama 3 and GPT-4 are both strong coding and problem-solving tools. Llama 3 can be a better option if you value efficiency and precision when coding. But GPT-4 stands out if you want help with creative chores like creating documentation or making code comments. In the end, the decision is based on your own needs and tastes.
Seems, Meta isn’t playing!
About Meta-AI’s Llama
Llama (Large Language Model Meta AI) is Meta’s response to the AI race dominated by proprietary models like OpenAI’s GPT series and Google’s Gemini. Unlike its competitors, Meta took a fully open-source approach, allowing developers, researchers, and enterprises to fine-tune and customize their AI models without restrictions.
The Llama series has been a major disruptor in the AI space due to its accessibility, lower computational costs, and strong natural language understanding capabilities. With each iteration, Meta has enhanced Llama’s efficiency, reasoning ability, and dataset size.
Llama 3.1– What’s the latest Update?
Llama 3.1 is Meta’s latest upgrade in the Llama series, designed to push the boundaries of open-source AI performance. Here’s what sets it apart:
Improved Model Efficiency
- Llama 3.1 features better training algorithms, allowing it to process language faster and with greater contextual awareness.
- Optimized for edge computing and mobile devices, making it more lightweight than its predecessors.
Enhanced Accuracy & Reduced Hallucinations
- Meta has introduced advanced fine-tuning techniques to make Llama 3.1 more reliable in generating factual responses.
- It outperforms earlier versions in complex reasoning tasks and long-form text generation.
Larger and More Diverse Training Data
- Compared to Llama 3.0, this version has been trained on a wider dataset, incorporating multilingual sources and domain-specific knowledge.
- Meta’s model aims to compete with GPT-4’s extensive dataset while maintaining an open-source advantage.
Stronger Customization Capabilities
- Businesses and developers can train Llama 3.1 on private datasets for tailored AI solutions.
- Unlike GPT-4’s closed API system, Llama allows full modification at a fundamental level.
Competitive Performance Benchmarks
- Early tests suggest Llama 3.1 rivals GPT-4 in several areas, particularly in text generation and reasoning.
- However, it still lags behind in certain tasks like code generation and multimodal processing.
Overview of GPT-4: OpenAI’s Flagship AI Model
GPT-4 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4) is OpenAI’s most advanced language model, designed to push the boundaries of natural language processing, reasoning, and multimodal capabilities. As the successor to GPT-3.5, it introduces significant improvements in accuracy, contextual understanding, and complex task execution.
Unlike Meta’s open-source Llama models, GPT-4 follows a proprietary and controlled approach, making it accessible only through OpenAI’s API and platforms like ChatGPT Plus, Microsoft Copilot, and other integrated services.
Superior Language Understanding & Context Retention
- GPT-4 exhibits a longer memory span, meaning it can handle larger prompts and maintain conversation flow better than its predecessors.
- Improved context awareness makes it better at following instructions, understanding nuanced queries, and generating coherent, human-like responses.
Multimodal Capabilities (GPT-4V)
- Unlike Llama 3.1, GPT-4 supports text and image processing, making it more versatile for AI applications like visual analysis, caption generation, and OCR (optical character recognition).
- GPT-4V (Vision) can analyze images and provide detailed descriptions, explanations, and context-based insights.
Higher Precision in Reasoning & Problem-Solving
- GPT-4 is trained to excel in logical reasoning, mathematical problem-solving, and structured thinking.
- It performs exceptionally well in competitive exams like SAT, LSAT, and coding challenges.
Stronger Guardrails for Bias & Safety
- OpenAI has integrated reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to ensure safer, unbiased, and responsible AI interactions.
- GPT-4 is less prone to hallucinations (incorrect or fabricated responses) compared to its predecessors.
Optimized for API & Enterprise Applications
- Unlike Llama 3.1, which requires on-premise deployment, GPT-4 is optimized for cloud-based usage via API integrations.
- This makes it the preferred choice for businesses looking for scalable AI solutions without managing infrastructure.
Also read: Top AI marketing tools better tha ChatGPT
Llama 3.1 vs. GPT-4: A Technical Comparison
Now that we have explored the fundamentals of Llama 3.1 and GPT-4, it’s time to analyze how they stack up against each other in terms of architecture, training methodology, performance, and real-world applications.
Model Architecture & Training Approach
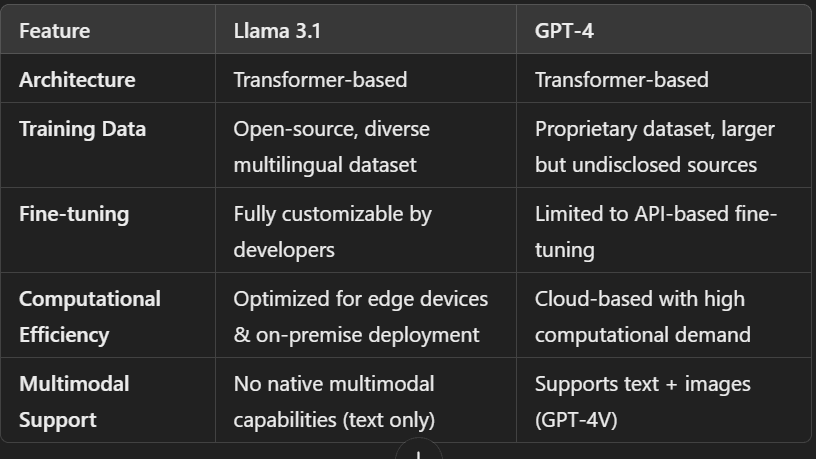
Key Takeaways
- Llama 3.1 gives developers more control over fine-tuning and custom datasets, making it ideal for enterprise customization.
- GPT-4’s multimodal capabilities give it an edge in vision-based AI applications like image recognition and medical AI.
- GPT-4 operates on proprietary, closed-access architecture, whereas Llama 3.1 remains open-source and customizable.
Performance in Key AI Benchmarks
To measure the real-world effectiveness of these models, we compare their performance across common AI benchmarks such as:
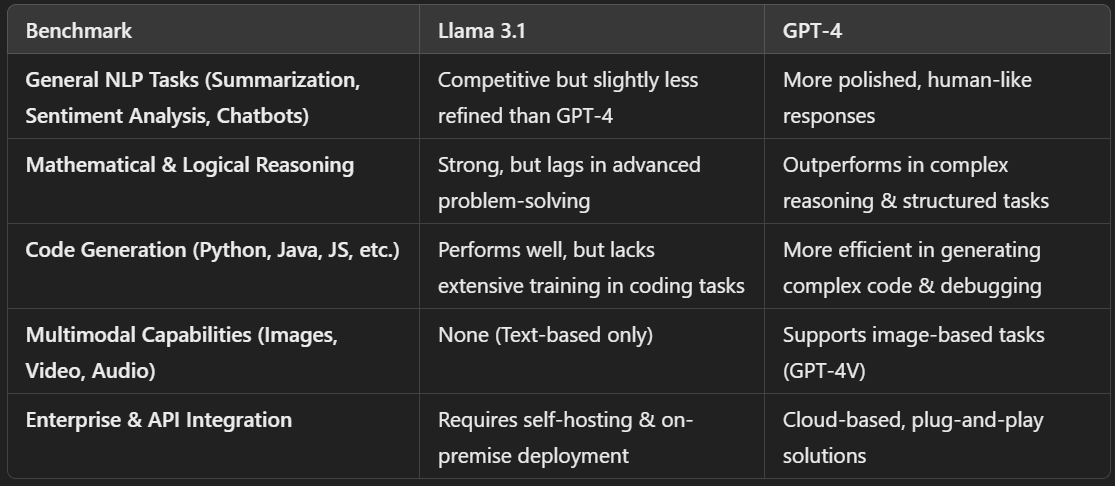
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4 is superior in complex problem-solving, logical reasoning, and structured code generation effective for prompt engineering.
- Llama 3.1, though slightly behind in NLP finesse, offers more flexibility for self-hosted AI applications.
- Llama 3.1 is lighter on computation, making it more accessible for local AI deployments.
Cost & Accessibility: Open-Source vs. Proprietary AI
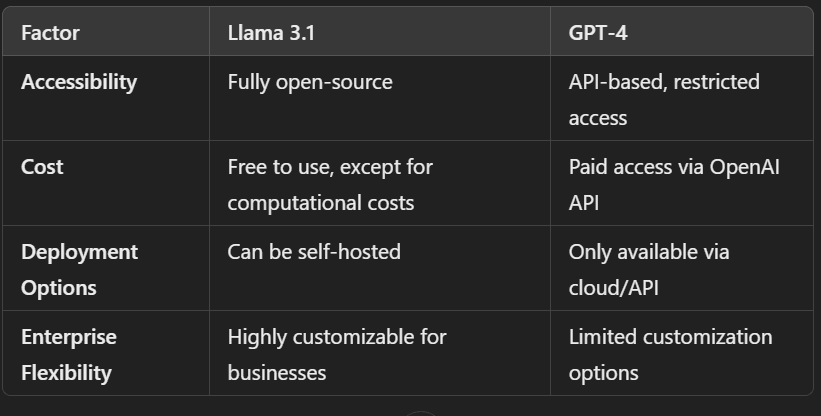
Key Takeaways
- Llama 3.1 is ideal for businesses that need full control over AI deployment and model fine-tuning.
- GPT-4 is better suited for companies looking for scalable, plug-and-play AI solutions with cloud support.
- The cost barrier of GPT-4 makes Llama 3.1 a more attractive choice for startups and research institutions.
Real-World Applications of Llama 3.1 and GPT-4
Now that we’ve explored the technical differences, let’s examine how Llama 3.1 and GPT-4 function in various industries. While both models are powerful, their unique architectures and accessibility make them better suited for different applications.
Enterprise AI & Business Solutions
Both Llama 3.1 and GPT-4 have found their way into businesses looking to optimize workflows, automate tasks, and enhance customer interactions.
Llama 3.1, being open-source and customizable, is a preferred choice for organizations that require self-hosted AI solutions for security-sensitive applications such as internal chatbots, knowledge management systems, and automation tools.
Companies handling confidential data—such as those in finance, healthcare, and law—can leverage Llama 3.1 to build proprietary AI assistants tailored to their specific needs.
On the other hand, GPT-4 excels in cloud-based AI integrations, making it an attractive option for enterprises looking for scalable AI solutions without requiring in-house development expertise.
Businesses in customer service, SaaS, and digital marketing benefit from its plug-and-play capabilities, allowing for seamless AI-driven automation.
Many companies use GPT-4 for automated customer support, generating reports, and personalizing user experiences with minimal effort.
Content Generation & the Media Industry
AI-driven content creation is reshaping digital marketing, journalism, and entertainment. GPT-4 is a dominant force in this space, offering unparalleled fluency and coherence in text generation.
It is widely used for blog writing, social media content, and creative storytelling. Its ability to generate persuasive, engaging, and contextually rich content makes it invaluable for brands, content creators, and marketing agencies.
Moreover, its multimodal capabilities (with GPT-4V) allow it to analyze and describe images, making it useful for ad creatives, video scripts, and campaign planning.
Llama 3.1, while powerful in text-based applications, lacks GPT-4’s fine-tuned fluency and multimodal support. However, it offers an edge for businesses and individuals looking for AI-assisted writing tools that can be customized.
Companies can train Llama 3.1 on domain-specific content, making it ideal for legal writing, research publications, and niche industry reports.
Although it may require more effort to fine-tune, its open-source nature allows content teams to develop AI models that align with their brand voice.
Software Development & AI Research
In the world of software development, AI models are increasingly being used for code generation, debugging, and automation.
GPT-4 outshines Llama 3.1 when it comes to coding assistance, offering developers structured, context-aware suggestions in multiple programming languages.
It is widely used in IDEs, coding platforms, and AI-powered development tools to assist in writing, optimizing, and debugging code.
Llama 3.1, while still effective, is better suited for AI research and private software projects that require custom training.
Research institutions and enterprises building proprietary software solutions benefit from its open-source architecture, which allows them to modify and optimize the model according to their specific needs.
Unlike GPT-4, which operates as a black box, Llama 3.1 provides researchers with full access to its model weights, making it an excellent choice for experimenting with AI architectures, training methodologies, and industry-specific AI applications.
Healthcare & Scientific Research
In healthcare and scientific research, AI is playing a transformative role in diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient care.
GPT-4 is widely adopted in medical AI applications due to its strong reasoning abilities, structured responses, and multimodal support.
It can process and analyze medical texts, assist in clinical decision-making, and even interpret medical images with GPT-4V.
AI-powered healthcare assistants, which help patients schedule appointments, understand symptoms, and manage chronic conditions, often rely on GPT-4’s advanced conversational abilities.
Llama 3.1, while not as refined for medical diagnosis, offers a significant advantage for medical research institutions looking for self-hosted AI solutions.
Many hospitals and research labs avoid using proprietary AI models due to data privacy concerns.
Llama 3.1 allows organizations to train AI on private medical datasets, making it a better option for in-house research on diseases, treatment optimization, and genomics.
The Future of AI with Llama & GPT
The race between Meta’s Llama and OpenAI’s GPT isn’t just about improving language models—it’s about shaping the future of AI accessibility, innovation, and ethics.
Both companies are pushing the boundaries of artificial intelligence, but their philosophies differ significantly: Llama focuses on open-source collaboration, while GPT champions proprietary AI with enterprise-level scalability.
So, where is AI headed with these two leading models?
The Future of Open-Source AI (Llama’s Evolution)
Meta’s commitment to open-source AI suggests a future where businesses, researchers, and independent developers have greater control over AI technology. With each iteration, Llama models are becoming more efficient, secure, and accessible, reducing the reliance on closed AI systems.
Llama 4 and Beyond:
We can expect Llama’s next versions to feature improved reasoning, better fine-tuning capabilities, and enhanced multimodal processing (integrating text, images, and potentially video/audio).
Wider Industry Adoption:
As enterprises move towards AI-driven automation, Llama’s open-source nature will make it the preferred choice for industries that require in-house AI solutions with full customization, such as healthcare, finance, and cybersecurity.
Decentralized AI:
The open-source movement is gaining momentum, and Meta’s Llama models could power decentralized AI applications, reducing dependency on big tech cloud-based AI services.
AI Democratization:
By keeping AI open, Meta is ensuring that startups and smaller players can access cutting-edge AI without paying premium API fees, encouraging innovation across industries.
Despite its advantages, the challenge for Llama will be keeping pace with GPT’s cutting-edge advancements in reasoning, memory, and multimodal capabilities while maintaining ethical AI usage and preventing misuse.
The Future of Proprietary AI (What’s Next for GPT?)
OpenAI’s GPT models have consistently pushed the limits of what AI can achieve, and GPT-5 is already rumored to bring groundbreaking advancements. The future of GPT-based AI lies in enhanced memory, real-time learning, and even greater multimodal interactions.
GPT-5 and Beyond:
The next evolution of GPT will likely feature long-term memory, allowing AI to retain context across multiple interactions, making it more human-like and personalized.
AI Assistants & AGI (Artificial General Intelligence):
OpenAI is working towards AGI, where AI can perform a broad range of cognitive tasks just like a human. Future GPT versions could be autonomous agents capable of making decisions, reasoning, and executing tasks with minimal human intervention.
Advanced Multimodal AI:
GPT-4 already introduced text and image understanding, but future models could integrate real-time voice recognition, video comprehension, and sensory AI, allowing fully interactive AI assistants.
AI in the Enterprise Sector:
OpenAI’s partnership with Microsoft and cloud integrations ensures that GPT-powered AI assistants will become a standard tool across industries, automating workflows in legal, finance, customer service, and software development.
However, OpenAI faces concerns over AI ethics, data privacy, and monopolization. As GPT models become smarter and more autonomous, regulatory scrutiny will increase, and businesses may seek alternative AI models like Llama for better control.
Final Thoughts
Rather than one model replacing the other, the future of AI may see both open-source and proprietary AI coexisting.
Llama will continue empowering developers, researchers, and privacy-conscious enterprises, while GPT will cater to businesses looking for AI with cutting-edge reasoning, automation, and scalability.
The question isn’t which model will dominate, but how AI will evolve to become more human-like, ethical, and integrated into our daily lives.
What’s next? AI is just getting started.
Interested in building an app infused with AI tool? Get intouch with DianApps custom software development services to get the best AI-driven solution!
Also read: DeepSeek vs ChatGPT- How do they compare?









Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *